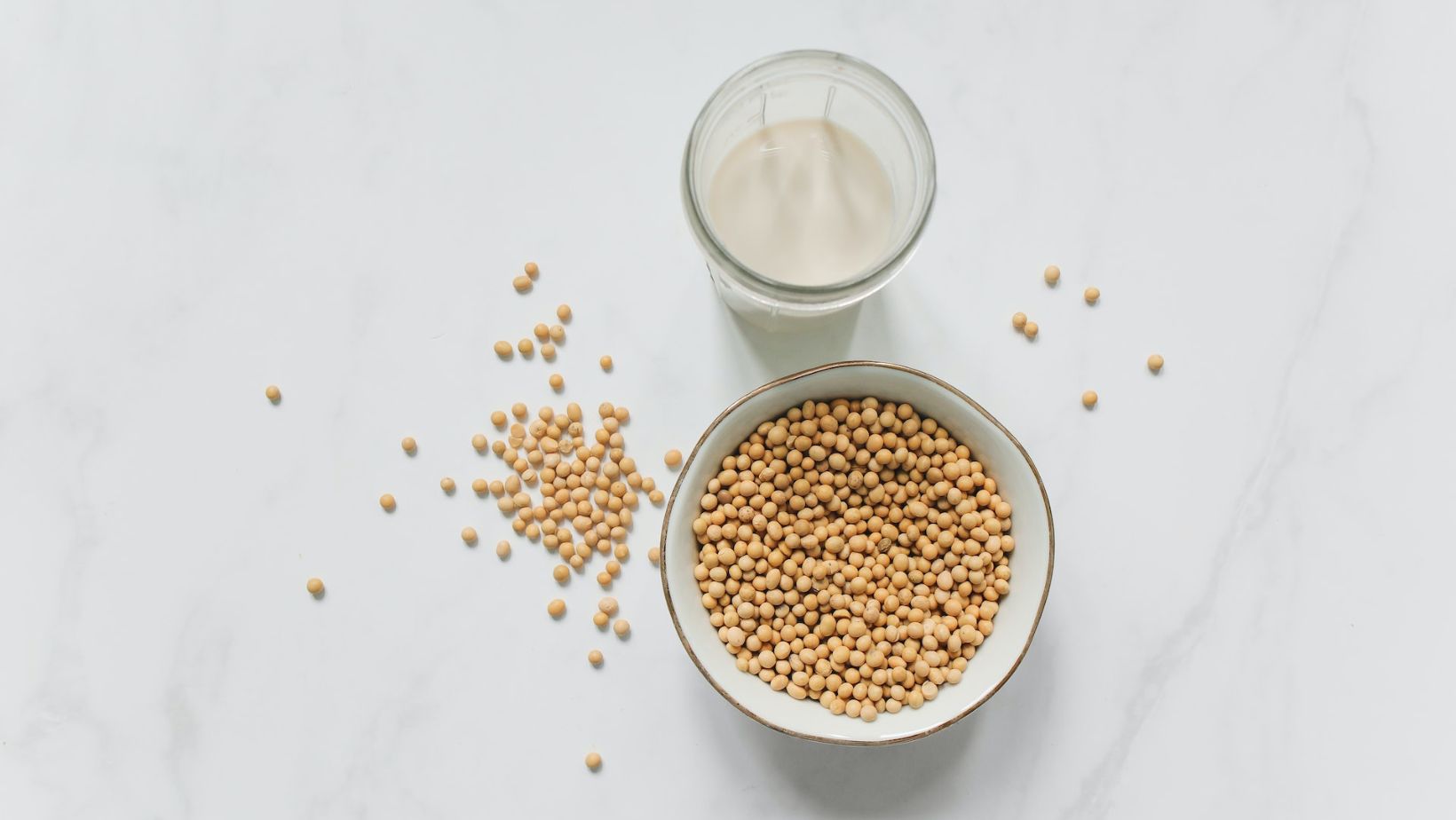
Soybean, an Asian native plant, is a protein-rich legume cultivated and consumed for over 13,000 years. It grows in pods enfolding edible seeds with yellow, black, or brown color. This legume is highly versatile and can be prepared into an extensive assortment of foods, comprising soy milk, soy protein, tempeh, tofu, soybean oil, soy flour, and miso. Soybeans consumed fresh from their pod are typically called edamame beans.
Soy products are rich in phytonutrients and antioxidants, and you can safely consume them multiple times a week to receive their multitude of health benefits. Among these benefits include reducing the effects of osteoporosis, taming hot flashes, and preventing hormonal cancers such as prostate and breast.
It’s vital to identify soy’s nutritional benefits and applications as it will help you discover the full power of soy. Therefore, this post will discuss six fundamental benefits of this nutrient-dense food and the nutritional value they bring into your life. Please continue reading to discover more about this legume.
What Are Soybeans?
Soybeans belong to the pea vegetable family and have been an Asian staple for thousands of years. animal protein products are immensely popular in vegan and vegetarian diets due to their high protein content and since you can process them into meat and milk alternatives. They are available in various colors, like:
- Black soybeans – Some Asian cultures use fermented or simmered black dishes in their traditional cuisines.
- Green soybeans – Young green soybeans are called edamame. People often steam and consume them as an appetizer straight from their pod. In addition, shelled edamame is available in soups, salads, and stir-fries.
- Yellow soybeans – many producers often use soybeans to produce soy milk, tamari, tempeh, and tofu. Moreover, they play a huge role in producing baking soy flour.
Soy possesses a hormone-like substance known as phytoestrogen, which imitates the effect of human estrogen and offers numerous health benefits. Consuming soy-based foods strengthens a person’s bones and helps minimize the risk of experiencing heart illnesses like stroke, coronary heart disease (CHD), cardiovascular disease, and some cancers.
Although soybeans comprise mostly protein, they also contain substantial fat and carbs. 100 grams of boiled soybeans contain:
- 18.2g protein
- 172 calories
- 8.4 g carbs
- 3g sugar
- 9g fat (1.3g saturated, 5.06g polyunsaturated, 1.98g monounsaturated)
- 6g fiber
Let’s discuss these nutrients in more detail.
Nutritional Value of Soy Products
1. Protein
Soybeans are the second-richest plant-based protein source. Their protein content is around 36% to 56% of their dry weight. Soy protein is impressive, but its quality is not as high as animal proteins. The major protein types in a soybean plant are conglycinin and glycinin, comprising around 80% of the protein content. As a result, these proteins could trigger some allergic effects in some people. To compensate for this, taking soy products can result in a modest reduction in cholesterol levels.
2. Minerals and Vitamins
Soy is rich in numerous minerals and vitamins, such as:
- Molybdenum – soybeans contain plenty of molybdenum, a vital trace element in seeds, legumes, and grains
- Folate – also called vitamin B9, this mineral has several functions, but it’s more important during and after pregnancy.
- Vitamin K1 – also called phylloquinone, this essential vitamin facilitates blood clotting.
- Manganese – soybeans are rich in manganese, a trace element often found in drinking water and food
- Thiamine – also called vitamin B1, thiamine is fundamental to a host of bodily processes, such as energy metabolism, as well as cell growth, functioning, and development.
![]()
3. Fat
Soybeans fall under the oilseed category and are used in producing soybean oil. They contain a fat content of around 18% of the soybean’s dry weight, mostly monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids, with trace amounts of saturated fat. Linoleic acid, accounting for more than half of the total fat content, is soy’s predominant type of fat.
4. Fiber
Soybeans have a reasonable quantity of insoluble and soluble fiber. Fiber is generally healthy and is fermented by useful bacteria in the colon. Once fermented, it produces short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), enhancing gut health and decreasing the risk of colon cancer.
5. Carbs
Since soybeans are low in carbs, they are very low on the GI (glycemic index). The GI measures how different foods impact a person’s sugar levels after a meal. Low GI is advantageous and is ideal for people struggling with diabetes.
Benefits of Soy
People consume soy in several ways – some are fermented, while others are unfermented. Fermented soy foods comprise miso, natto, soy sauce, and tempeh.

On the other hand, unfermented soy foods include soymilk, tofu, soy nuts, sprouts, and edamame. Here are the main advantages of consuming soy products:
1. Contain Protective Antioxidants
Soy products contain a group of natural compounds known as isoflavones. Isoflavones are polyphenols with strong antioxidants, reducing the damage that free radicals cause through oxidative stress. Oxidative stress is a key component in the onset of chronic illnesses and aging. Soy products help your skin look brighter and younger due to the isoflavones and other active plant compounds like saponins.
2. Relieve Menopausal Symptoms
Soybean isoflavones have gained tremendous popularity in the research and development industry. Notably, some studies indicate that consuming a soy-rich diet frequently can decrease the risk of breast cancer. They do so because the phytoestrogen imitates the human estrogen and its effect on the body. In addition, several women find soy products soothing when experiencing perimenopause symptoms like hot flashes or poor moods.
3. Complete Source of Protein
To be a complete source of protein means having all nine essential amino acids the human body requires for repair, growth, and physiological functions like immunity. Soy products are an excellent protein source, especially for people adhering to vegetarian and vegan diets. Unlike most plant-based foods, which contain limited protein amounts, soy meal is a superior protein with a great combination of essential and non-essential amino acids.
4. Are Heart-Friendly
Consuming a meal with soy foods often reduces the risk of contracting cardiovascular diseases, such as coronary heart disease and stroke. They substantially reduce two primary risk factors for heart disease – LDL cholesterol levels and total cholesterol.
According to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), adults consuming around four servings of soy daily could reduce LDL cholesterol levels by around 3% to 5%.
Concluding Thoughts
Soy is a protein-rich legume native to Asia and a decent source of fat and carbs. Its products are rich in minerals, vitamins, and beneficial plant compounds, like isoflavones. Therefore, depending on your protein needs, you can incorporate it into your regimen. You may need more if you’re a vegan because few plant-based products contain as much protein as soy.
You must understand this legume’s nutritional value and benefits to determine how it can improve your nutritional needs. Therefore, use this guide to discover the essential information you need to know about this amazing legume.
