Injection molding is one of the most efficient methods for manufacturing plastic parts. It is favored for its ability to facilitate large production runs of identical parts. The process, though seemingly complicated, is quite straightforward in its simplest form as it only requires two steps: obtaining the mold and using it to create parts. In almost every case, it is the least expensive way to produce parts in medium to high volumes. This makes it ideal for companies looking to manufacture high-quality products without breaking the bank. Once the mold is made, it can be used repeatedly, producing consistent results at a low cost, making the entire process not only efficient but also scalable. Moreover, it allows for a variety of molding techniques, including abs plastic molding, which is popular for its durability and strength.
Once the initial mold is made, the price-per-unit cost of injection molding becomes comparatively low, making it a cost-effective choice for manufacturing. This method creates identical, perfectly molded products every time, which significantly cuts waste material when compared to other processes like CNC machining. These are some of the main reasons why plastic injection molding is a rapidly growing industry, valued at $258.2 billion in 2019 and predicted to reach a valuation of $372.9 billion in less than a decade. Its efficiency and scalability make it an attractive option for businesses looking to produce high-quality parts consistently.
Plastic injection molding is a process that requires a high level of precision to ensure the quality of the final product. To create parts using injection molding, manufacturers must follow specific steps. Each step is crucial to achieving consistent results, as this technique demands careful control over materials and equipment. By maintaining strict standards, manufacturers can produce high-quality parts with minimal errors, making injection molding a reliable method for mass production.
A Note Regarding the Tooling Process
While injection molding offers many advantages, the process is not without drawbacks. One major challenge is the upfront tooling costs and the significant lead time required. These can be obstacles for manufacturers, as the tooling is a crucial and heavily-involved undertaking that needs to be completed once for each product. It is often considered the first phase of the injection molding process, but for practical purposes, it’s better to view it separately. Despite these challenges, once the tooling is ready, the production becomes efficient and cost-effective, making it worth the initial investment.
Understanding the Tooling Process in Injection Molding
The tooling phase is crucial because it requires product design teams to carefully design and prototype each part. Often, 3D printing is used to quickly create a prototype, but the real challenge lies in crafting a mold that can reliably make the final part.
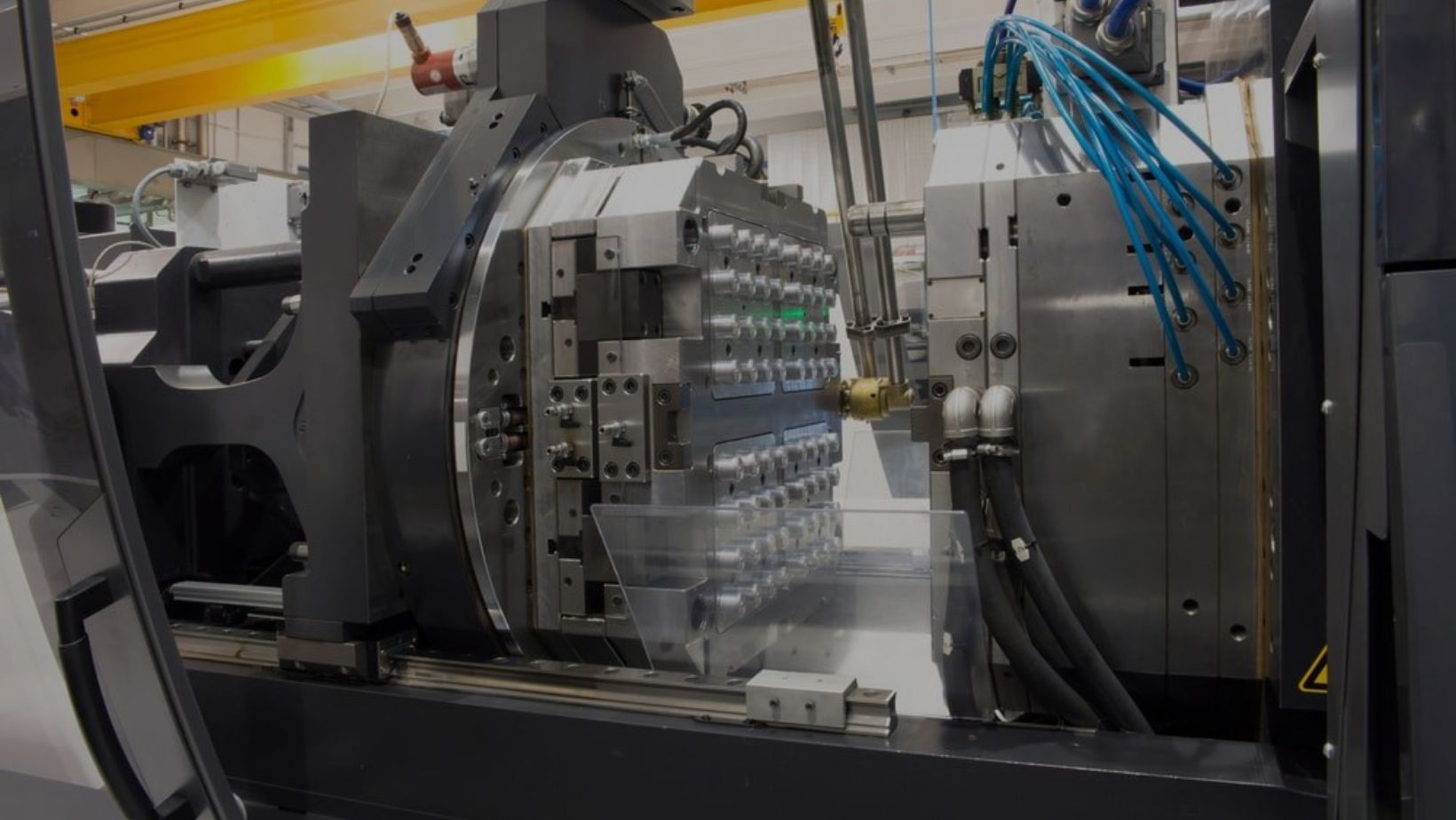
This step requires extensive testing and optimizing to ensure the mold is perfect before moving on to the actual injection molding process. Once the mold is complete, the same process can be completed thousands of times to create identical parts efficiently. The ability to make parts connection smooth and precise during this phase is crucial for ensuring the integrity of the final product.
The Injection Molding Process Steps
Once the mold is created, the injection molding process becomes an easily-repeatable method for producing parts. This efficient process is structured around six discrete steps, each crucial to ensuring high-quality results. The consistency offered by this technique makes it ideal for large-scale production, as it allows manufacturers to replicate the exact same part over and over again without compromising on precision.
Clamping
The first step in the injection molding process is known as clamping. In this phase, injection molds, which are typically made of two clamshell-style pieces, are tightly pressed together. These two metal plates of the mold are pushed against each other using a powerful machine press. This ensures that the mold is securely closed and ready for the next phase, preventing any material from leaking out during the injection.
Injection
Once the two plates of the mold are securely clamped together, the injection process can begin. The plastic, which is typically in the form of granules or pellets, is first melted into a complete liquid state. This liquid is then injected into the mold cavity. At this stage, it is crucial for manufacturers to ensure that the temperature remains constant throughout this step of the process. This stability helps in creating a uniform product without defects, making it a critical phase in injection molding.
Dwelling
In the dwelling phase, the melted plastic is carefully injected to fill the entirety of the mold. At this stage, pressure is applied directly to the mold to ensure that the liquid reaches and fills every cavity.
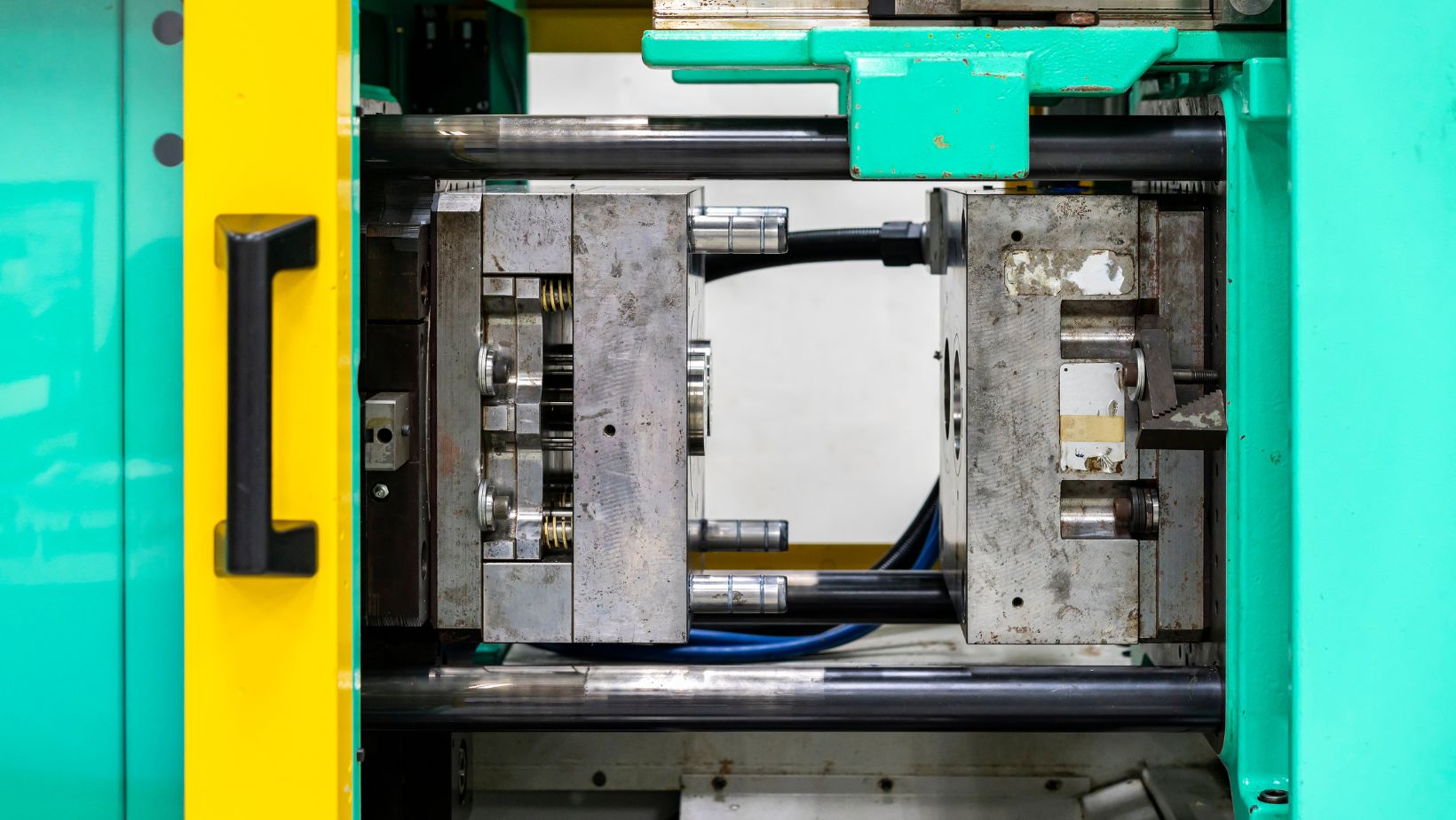
This step is essential to make sure the final product is an identical copy of the original mold design. Achieving this precision is crucial for maintaining the quality and consistency of the molded parts.
Cooling
The cooling stage is the most straightforward part of the injection molding process. Once the mold is filled, it is left alone so the hot plastic inside can gradually cool and solidify into its final shape. This allows the creation of a usable product that can be safely removed from the mold without damage. Proper cooling is essential to ensure the molded part retains its quality and dimensions, making it ready for use or further processing.
Mold Opening
Once the part has cooled, the clamping motor will slowly open the two parts of the mold. This careful process ensures a safe and simple removal of the final product. Proper handling during this phase is crucial to avoid any damage to the newly formed piece, ensuring that it meets the required quality standards and is ready for use.
Ejection
After the mold is open, an ejector bar will slowly push the solidified product out of the open mold cavity. The fabricator then uses cutters to eliminate any waste material and refine the piece to create a perfect final product ready for customer use. Often, this waste material can be recycled and reinjected for the next part, effectively decreasing material costs and minimizing waste. This approach not only ensures high-quality products but also promotes sustainable manufacturing practices. Advanced techniques, like overmold, can also be integrated at this stage to enhance the final product’s functionality.
A Partner in Injection Molding
Choosing a partner for injection molding can seem like an intimidating prospect due to the time and cost involved in the tooling phase. However, once the first mold is created, it becomes the easiest way to create countless identical parts at a relatively low cost. This is why injection molding remains one of the fastest-growing practices in manufacturing today. With the right partner, companies can efficiently produce high-quality products, keeping both costs and production time manageable.